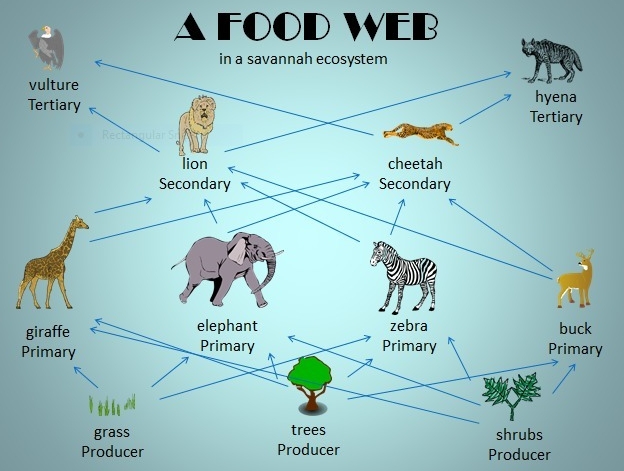
Animals have adapted to survive in a variety of environments, leading to diverse diets among different species. From carnivores to herbivores, each animal has specific dietary needs that help them thrive in their habitats.
Carnivores: Masters of the Hunt
Carnivores are meat-eating animals that primarily rely on hunting and consuming other animals for sustenance. These predators have sharp teeth and claws to capture and kill their prey. Examples of carnivores include lions, wolves, and eagles.
Herbivores: Plant-Based Eaters
Herbivores are animals that feed exclusively on plants and vegetation. These animals have flat teeth for grinding plant matter and long digestive systems to break down tough plant fibers. Examples of herbivores include deer, cows, and rabbits.
Omnivores: The Balanced Eaters
Omnivores have a diet that consists of both plants and animals. These animals are opportunistic eaters that can adapt to various food sources depending on availability. Examples of omnivores include bears, raccoons, and humans.
Insectivores: Feasting on Insects
Insectivores are animals that primarily consume insects and other small invertebrates. These animals have specialized features such as long tongues or sharp beaks to catch and eat their prey. Examples of insectivores include anteaters, frogs, and bats.
Frugivores: Fruit Lovers
Frugivores are animals that have a diet consisting mainly of fruits and berries. These animals play a crucial role in seed dispersal by consuming fruits and spreading the seeds in their droppings. Examples of frugivores include birds, primates, and bats.
Piscivores: Fish-Eating Specialists
Piscivores are animals that primarily feed on fish and other aquatic creatures. These predators have streamlined bodies and sharp teeth for catching and consuming their prey. Examples of piscivores include dolphins, herons, and penguins.
Each animal’s diet is a result of millions of years of evolution and adaptation to their specific ecological niche. By examining the diverse diets of animals, we can gain a better understanding of the interconnectedness of ecosystems and the importance of biodiversity in maintaining a healthy planet.